Learn all about fibroids.
WHAT ARE FIBROIDS?
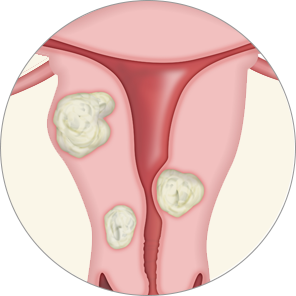
Fibroids, also known as uterine fibroids, leiomyomas, or myomas, are benign (non-cancerous) tumors that grow within the muscle tissue of the uterus.

WHO IS AT RISK?
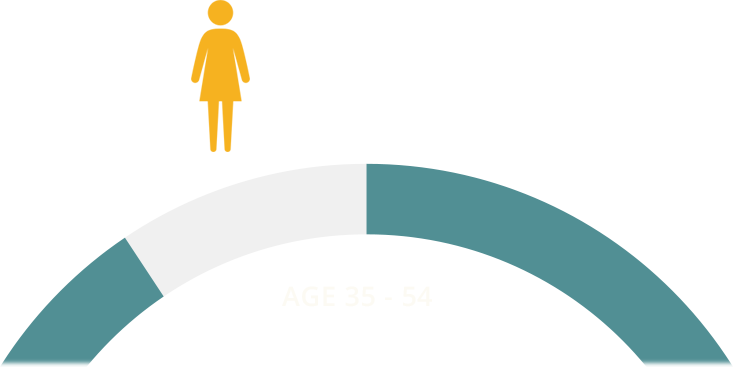
Since uterine fibroids are the most common tumors within the female reproductive system, all women are at a potential risk of developing them.
The majority of uterine fibroids are diagnosed in women between the ages of 35 and 54. However, fibroids can occur in women younger than 35.
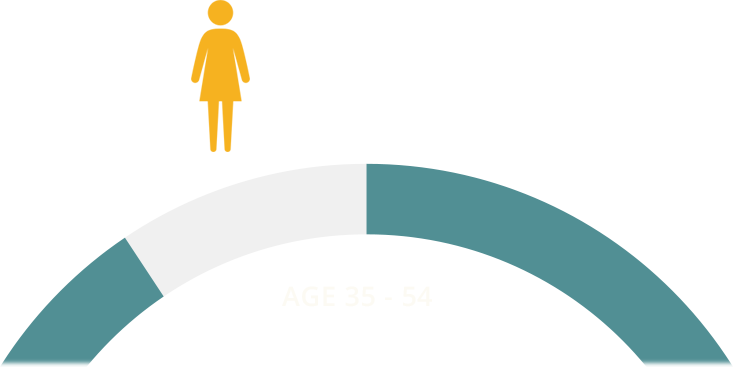
WHAT DOES THE RESEARCH SAY?
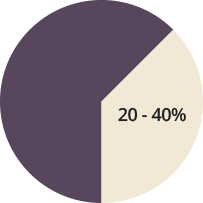
Studies demonstrate the prevalence of fibroids in 20-40% of women older than 35 years of age.1
Fibroids vary in size and can be as small as a seed, as big as a melon, and anywhere in between.

Most clinicians believe fibroids shrink when a woman goes through menopause.
REFERENCES:
- Wallach, E. E. (1992). Myomectomy. In Thompson, J. D., & Rock, J. A. (Eds.), Te Linde’s Operative Gynecology, 7th (pp. 647-662). Philadelphia: J. B. Lippincott.
UNCOMFORTABLE WITH
A HYSTERECTOMY?
A HYSTERECTOMY?
Learn about UFE.

